bRPC源码解析·bthread调度执行流程
(作者简介:KIDGINBROOK,在昆仑芯参与训练框架开发工作)
整体流程
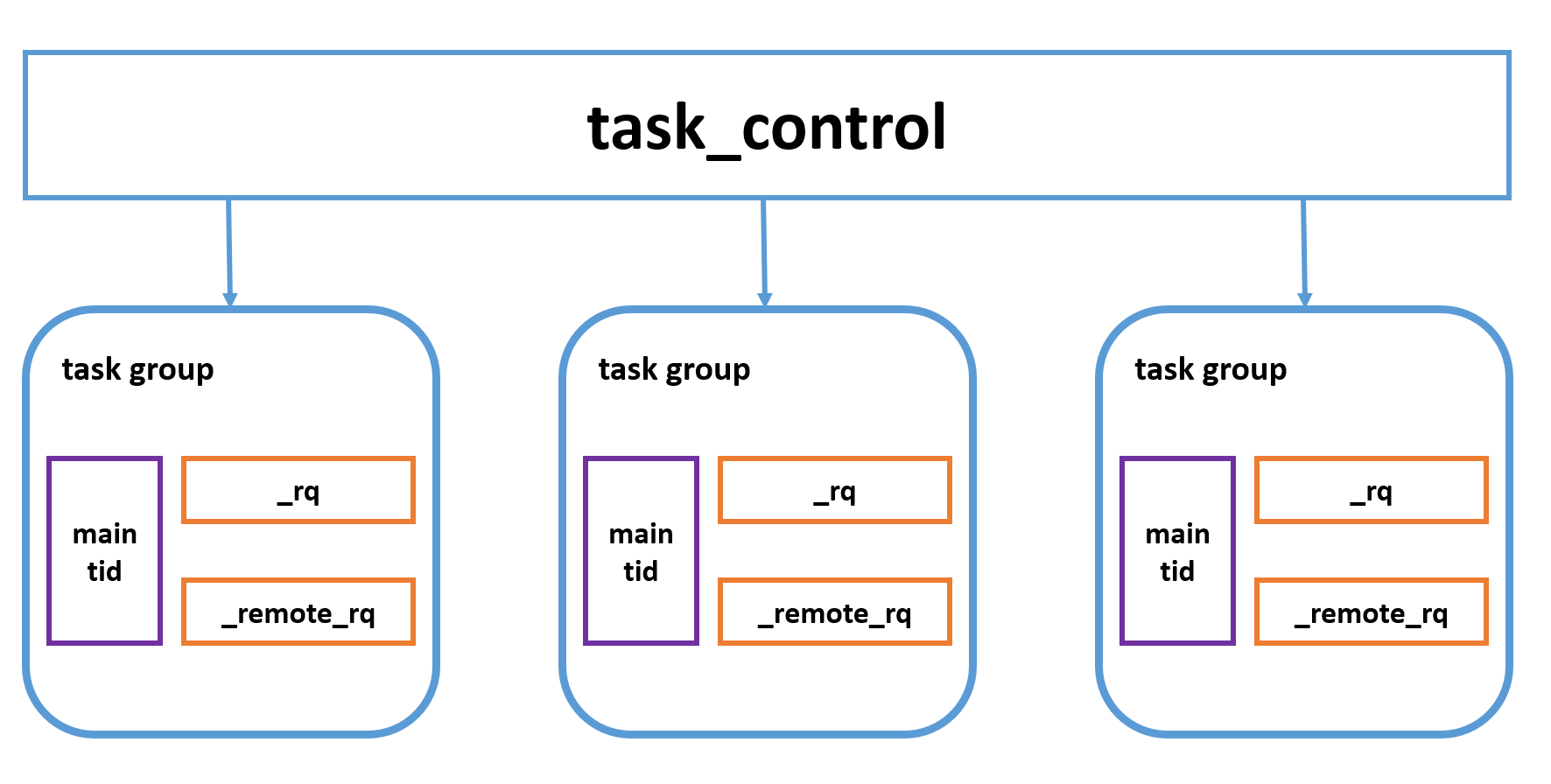
task_group负责对bthread的调度执行,一个task_group对应一个pthread,内部有两个执行队列,分别为_rq和_remote_rq,执行队列中存放着待执行的bthread,bthread创建的bthread会被存放在_rq,pthread创建的bthread会被存放在_remote_rq。task_control为全局单例,内部有多个task_group。
主要接口
TaskControl
TaskControl是一个单例,下面是初始化的过程,主要逻辑即为创建_concurrency个worker(bthread_worker)线程,每个worker执行worker_thread函数
int TaskControl::init(int concurrency) {
_concurrency = concurrency;
_workers.resize(_concurrency);
for (int i = 0; i < _concurrency; ++i) {
const int rc = pthread_create(&_workers[i], NULL, worker_thread, this);
...
}
...
}
worker_thread的逻辑为通过create_group创建一个TaskGroup g,添加到TaskControl中,设置tls_task_group为g,tls_task_group为tls变量,因此只有worker线程的tls_task_group为非null,然后执行TaskGroup的run_main_task函数
void* TaskControl::worker_thread(void* arg) {
TaskControl* c = static_cast<TaskControl*>(arg);
TaskGroup* g = c->create_group();
...
tls_task_group = g;
c->_nworkers << 1;
g->run_main_task();
...
}
TaskGroup* TaskControl::create_group() {
...
g->init(FLAGS_task_group_runqueue_capacity);
...
}
TaskGroup
TaskGroup对应一个pthread,初始化函数如下,创建rq和remote_rq,都是负责存放待执行bthread的队列,然后创建main_stack和main_tid,main_tid代表主流程对应的bthread id,后面会具体讲main_stack和main_tid的作用。TaskMeta为一个bthread的meta信息,如执行函数,参数,local storage等,这里会将cur_meta设置为main_tid对应的TaskMeta。
int TaskGroup::init(size_t runqueue_capacity) {
_rq.init(runqueue_capacity);
_remote_rq.init(runqueue_capacity / 2);
ContextualStack* stk = get_stack(STACK_TYPE_MAIN, NULL);
...
butil::ResourceId<TaskMeta> slot;
TaskMeta* m = butil::get_resource<TaskMeta>(&slot);
...
m->stop = false;
m->interrupted = false;
m->about_to_quit = false;
m->fn = NULL;
m->arg = NULL;
m->local_storage = LOCAL_STORAGE_INIT;
m->cpuwide_start_ns = butil::cpuwide_time_ns();
m->stat = EMPTY_STAT;
m->attr = BTHREAD_ATTR_TASKGROUP;
m->tid = make_tid(*m->version_butex, slot);
m->set_stack(stk);
_cur_meta = m;
_main_tid = m->tid;
_main_stack = stk;
_last_run_ns = butil::cpuwide_time_ns();
return 0;
}
每个worker会一直在while循环中,如果有可执行的bthread,wait_task会返回对应bthread的tid,否则当前worker会阻塞;wait_task的具体逻辑是先去当前task_group的_remote_rq中pop,如果没有,则去其他的task_group的_rq和_remote_rq中pop。
void TaskGroup::run_main_task() {
bvar::PassiveStatus<double> cumulated_cputime(
get_cumulated_cputime_from_this, this);
std::unique_ptr<bvar::PerSecond<bvar::PassiveStatus<double> > > usage_bvar;
TaskGroup* dummy = this;
bthread_t tid;
while (wait_task(&tid)) {
TaskGroup::sched_to(&dummy, tid);
DCHECK_EQ(this, dummy);
DCHECK_EQ(_cur_meta->stack, _main_stack);
if (_cur_meta->tid != _main_tid) {
TaskGroup::task_runner(1/*skip remained*/);
}
}
}
当拿到可执行的tid后,调用sched_to,首先通过tid拿到该tid对应的TaskMeta,如果已经为该meta分配过栈,则调用sched_to(pg, next_meta),该函数的主要逻辑为通过jump_stack(cur_meta->stack, next_meta->stack)跳转至next_meta;否则通过get_stack分配一个新栈,并设置该栈的执行入口为task_runner函数。
inline void TaskGroup::sched_to(TaskGroup** pg, bthread_t next_tid) {
TaskMeta* next_meta = address_meta(next_tid);
if (next_meta->stack == NULL) {
ContextualStack* stk = get_stack(next_meta->stack_type(), task_runner);
if (stk) {
next_meta->set_stack(stk);
} else {
// stack_type is BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD or out of memory,
// In latter case, attr is forced to be BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD.
// This basically means that if we can't allocate stack, run
// the task in pthread directly.
next_meta->attr.stack_type = BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD;
next_meta->set_stack((*pg)->_main_stack);
}
}
// Update now_ns only when wait_task did yield.
sched_to(pg, next_meta);
}
task_runner核心如下,首先执行remain函数,remain为一个bthread在开始运行自己逻辑前需要做的一些工作,后面会看到;然后执行该meta的函数,因为函数执行过程中该bth可能会调度至其他worker,因此task_group可能发生改变,所以执行完成后重新对g进行设置;最后调用ending_sched。
void TaskGroup::task_runner(intptr_t skip_remained) {
// NOTE: tls_task_group is volatile since tasks are moved around
// different groups.
TaskGroup* g = tls_task_group;
if (!skip_remained) {
while (g->_last_context_remained) {
RemainedFn fn = g->_last_context_remained;
g->_last_context_remained = NULL;
fn(g->_last_context_remained_arg);
g = tls_task_group;
}
}
do {
TaskMeta* const m = g->_cur_meta;
try {
thread_return = m->fn(m->arg);
} catch (ExitException& e) {
thread_return = e.value();
}
// Group is probably changed
g = tls_task_group;
...
g->set_remained(TaskGroup::_release_last_context, m);
ending_sched(&g);
} while (g->_cur_meta->tid != g->_main_tid);
// Was called from a pthread and we don't have BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD
// tasks to run, quit for more tasks.
}
ending_sched会尝试获取一个可执行的bth,如果没有的话,则下一个执行的则为main_tid对应的meta;然后通过上述的sched_to(next_meta)跳转到next_meta。
void TaskGroup::ending_sched(TaskGroup** pg) {
TaskGroup* g = *pg;
bthread_t next_tid = 0;
// Find next task to run, if none, switch to idle thread of the group.
#ifndef BTHREAD_FAIR_WSQ
// When BTHREAD_FAIR_WSQ is defined, profiling shows that cpu cost of
// WSQ::steal() in example/multi_threaded_echo_c++ changes from 1.9%
// to 2.9%
const bool popped = g->_rq.pop(&next_tid);
#else
const bool popped = g->_rq.steal(&next_tid);
#endif
if (!popped && !g->steal_task(&next_tid)) {
// Jump to main task if there's no task to run.
next_tid = g->_main_tid;
}
TaskMeta* const cur_meta = g->_cur_meta;
TaskMeta* next_meta = address_meta(next_tid);
if (next_meta->stack == NULL) {
if (next_meta->stack_type() == cur_meta->stack_type()) {
// also works with pthread_task scheduling to pthread_task, the
// transfered stack is just _main_stack.
next_meta->set_stack(cur_meta->release_stack());
} else {
ContextualStack* stk = get_stack(next_meta->stack_type(), task_runner);
if (stk) {
next_meta->set_stack(stk);
} else {
// stack_type is BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD or out of memory,
// In latter case, attr is forced to be BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD.
// This basically means that if we can't allocate stack, run
// the task in pthread directly.
next_meta->attr.stack_type = BTHREAD_STACKTYPE_PTHREAD;
next_meta->set_stack(g->_main_stack);
}
}
}
sched_to(pg, next_meta);
}
main tid
然后说下开始提到的main_tid/main_stack,task_group是一个pthread,在执行bthread时,会运行在该bthread栈中,其他时刻都是运行在pthread栈中。brpc并没有为pthread重新分配一个栈,而是仅仅记录了pthread栈的位置,main_stack即为pthread栈,而main_tid则代表了这个pthread。
下面来看下是如何实现这一过程的
int TaskGroup::init(size_t runqueue_capacity) {
...
ContextualStack* stk = get_stack(STACK_TYPE_MAIN, NULL);
...
}
在上面TaskGroup::init中,可以看到ContextualStack* stk = get_stack(STACK_TYPE_MAIN, NULL); STACK_TYPE_MAIN即为main_stack的类型,get_stack会调用StackFactory的get_stack,StackFactory是个模板类,get_stack会分配栈空间,然后针对STACK_TYPE_MAIN做了特化,此时不会分配栈空间,仅仅返回一个ContextualStack对象;
template <> struct StackFactory<MainStackClass> {
static ContextualStack* get_stack(void (*)(intptr_t)) {
ContextualStack* s = new (std::nothrow) ContextualStack;
if (NULL == s) {
return NULL;
}
s->context = NULL;
s->stacktype = STACK_TYPE_MAIN;
s->storage.zeroize();
return s;
}
static void return_stack(ContextualStack* s) {
delete s;
}
};
然后在切换到bthread执行的过程中,会调用jump_stack(cur_meta->stack, next_meta->stack)
inline void jump_stack(ContextualStack* from, ContextualStack* to) {
bthread_jump_fcontext(&from->context, to->context, 0/*not skip remained*/);
}
cur_meta此时为main_tid对应的taskmeta,next_meta为即将要执行的meta;由前面文章可知bthread_jump_fcontext执行时,会将当前各个寄存器push到当前栈中,即pthread栈,然后将esp赋值给(rdi),即from->context,因此main_tid的stack便指向了pthread栈。
主要接口
接下来看下bthread提供的接口,以bthread_start_urgent和bthread_start_background为例,如函数名所示,前者对新建的bthread以”高优先级”处理,后者以”低优先级”处理,后面会看到优先级的意思。首先看下bthread_start_urgent
bthread_start_urgent
int bthread_start_urgent(bthread_t* __restrict tid,
const bthread_attr_t* __restrict attr,
void * (*fn)(void*),
void* __restrict arg) {
bthread::TaskGroup* g = bthread::tls_task_group;
if (g) {
// start from worker
return bthread::TaskGroup::start_foreground(&g, tid, attr, fn, arg);
}
return bthread::start_from_non_worker(tid, attr, fn, arg);
}
由上可知,tls_task_group为tls,普通pthread的tls_task_group为null,先以普通pthread看下整体流程;此时普通pthread会调用start_from_non_worker。
BUTIL_FORCE_INLINE int
start_from_non_worker(bthread_t* __restrict tid,
const bthread_attr_t* __restrict attr,
void * (*fn)(void*),
void* __restrict arg) {
TaskControl* c = get_or_new_task_control();
if (NULL == c) {
return ENOMEM;
}
if (attr != NULL && (attr->flags & BTHREAD_NOSIGNAL)) {
// Remember the TaskGroup to insert NOSIGNAL tasks for 2 reasons:
// 1. NOSIGNAL is often for creating many bthreads in batch,
// inserting into the same TaskGroup maximizes the batch.
// 2. bthread_flush() needs to know which TaskGroup to flush.
TaskGroup* g = tls_task_group_nosignal;
if (NULL == g) {
g = c->choose_one_group();
tls_task_group_nosignal = g;
}
return g->start_background<true>(tid, attr, fn, arg);
}
return c->choose_one_group()->start_background<true>(
tid, attr, fn, arg);
}
start_from_non_worker会尝试获取taskcontrol单例,如果没有则创建一个,并初始化好一定数量的taskgroup;然后选择一个taskgroup,调用start_background
template <bool REMOTE>
int TaskGroup::start_background(bthread_t* __restrict th,
const bthread_attr_t* __restrict attr,
void * (*fn)(void*),
void* __restrict arg) {
...
butil::ResourceId<TaskMeta> slot;
TaskMeta* m = butil::get_resource(&slot);
...
m->fn = fn;
m->arg = arg;
...
if (REMOTE) {
ready_to_run_remote(m->tid, (using_attr.flags & BTHREAD_NOSIGNAL));
} else {
ready_to_run(m->tid, (using_attr.flags & BTHREAD_NOSIGNAL));
}
return 0;
}
REMOTE表示创建该bthread的线程是普通pthread还是bthread_worker,函数主要逻辑为创建taskmeta,然后调用ready_to_run_remote将该tid加入到taskgroup的remote_rq中。
然后看下bthread_worker调用bthread_start_urgent的过程,这种场景其实是在bthread中创建bthread,此时会调用start_foreground,然后创建taskmeta,并直接切换到这个新的bthread运行,即”高优先级”。
int TaskGroup::start_foreground(TaskGroup** pg,
bthread_t* __restrict th,
const bthread_attr_t* __restrict attr,
void * (*fn)(void*),
void* __restrict arg) {
...
TaskGroup* g = *pg;
g->_control->_nbthreads << 1;
if (g->is_current_pthread_task()) {
// never create foreground task in pthread.
g->ready_to_run(m->tid, (using_attr.flags & BTHREAD_NOSIGNAL));
} else {
// NOSIGNAL affects current task, not the new task.
RemainedFn fn = NULL;
if (g->current_task()->about_to_quit) {
fn = ready_to_run_in_worker_ignoresignal;
} else {
fn = ready_to_run_in_worker;
}
ReadyToRunArgs args = {
g->current_tid(),
(bool)(using_attr.flags & BTHREAD_NOSIGNAL)
};
g->set_remained(fn, &args);
TaskGroup::sched_to(pg, m->tid);
}
return 0;
}
start_foreground最后,这里会设置当前task_group的remain,上文提到在task_runner中,bthread在真正执行自己meta的逻辑前会先执行remain,start_foreground会抢占当前bthread的执行,因此通过remain将当前bthread重新push到rq中等待执行。
bthread_start_background
接口bthread_start_background对于普通pthread的情况和bthread_start_urgent一致;而对于bthread_worker则会调用start_background